ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)
What is the biological intelligence?
Cognitive sciences study human intelligence. Cognitive sciences have made it possible to identify the different mechanisms that are at work in the functioning of thought; this thought that allows us to speak, to move, to memorize, to reason, to plan, to be abstract or creative.
For Frederic Alexandre who is an INRIA researcher in computational neuroscience, biological intelligence is an addition of different abilities:
- To be able to respond quickly to a complex situation.
- To be able to find the satisfactory rather than the optimal answer.
- To be able to find what is important in a piece of information.
- To be able to adapt when conditions change.
- To be able to react quickly to an unexpected situation.
The strength of biological intelligence is the complementarity of these emotional and logical abilities.
How do we learn?
There are two main ways of learning, the one that comes from knowledge transmission, and the one that comes from the experience that we acquire. Artificial intelligence researchers are attempting to implement these ways of learning on machines. This is what we call artificial intelligence (AI).
AI Approaches
The symbolic approach is to imitate how a human being is thinking and uses their knowledge. What we learn is given to us by the transmission of knowledge, rules, and procedures (how to make an addition for example). This is mostly how we learn at school. This approach has given the expert systems.
In artificial intelligence, an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert. Expert systems can’t adapt themselves when conditions change, they are specialized, as the INRIA researcher Frederic Alexandre says, “a program that can beat the chest world champion is unable to recognize a duck”.
The connectionist approach is to imitate how a human being learn from their experiences like how one learns to ride a bike or to recognize a duck. This approach is favored today, it has given what we call machine learning or deep learning AI.
Machine learning AI
Machine learning algorithms use some fields of math like statistics, probabilities, and algebra functions to find logical rules between X data (features) and Y data (targets). The match between X and Y often takes the form of a prediction score which should be as close as possible to 100%, the algorithms are self-modifying to obtain the best possible score.
For example, imagine an algorithm that tells you if a photo shows a woman or a man. X pieces of data are the features of each person (height, geometric shapes, face hair, etc.) and Y are categories (man, woman).
First, we give a data set (different photos) to the algorithm for it to build a mathematical relation between X and Y for each photo. This is the learning phase.
When this phase is over, we give a training set of photos to the algorithm. The training set of photos is different from the initial data set. The algorithm uses the mathematical relation built during the training phase and gives a score like 70% chance to be a female. If the answer is correct for enough photos, the algorithm is operational.
Deep learning is a kind of machine learning based on artificial neural networks. Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs), are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains.
There are different possible strategies to teach the algorithm:
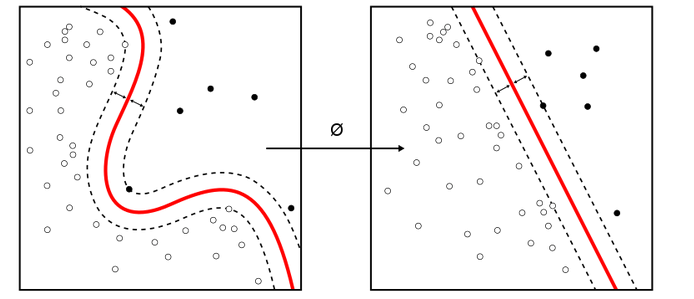
Supervised learning: the data is annotated (man, woman) during the training session. The math operations can produce a classification with a boundary (in red below) between men and women for example:
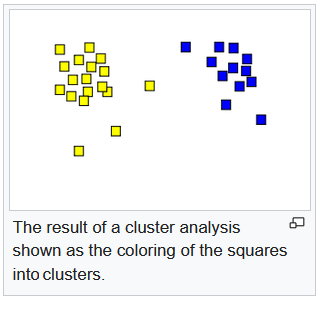
Unsupervised learning: the algorithm is not provided with any pre-assigned labels for the training data. As a result, unsupervised learning algorithms must first self-discover patterns in the training data set.
Reinforcement learning: the program learns by improving, thanks to a reward system. This method resembles motivational learning used in animal husbandry.
The more points the algorithm gets for following a direction or performing an action, the more it strengthens its decision.
Generative artificial intelligence (AI)
GAI is artificial intelligence capable of generating text, images, or other media, using generative models. Generative AI models learn the patterns and structure of their input training data and then generate new data that has similar characteristics.
In the early 2020s, advances in transformer-based deep neural networks enabled a number of generative AI systems notable for accepting natural language prompts as input. These include large language model chatbots such as ChatGPT.
AI Concerns
The development of generative AI has raised concerns from governments, businesses, and individuals, resulting in protests, legal actions, calls to pause AI experiments, and actions by multiple governments.
In April 2023, it was reported that image generation AI has resulted in 70% of the jobs for video game illustrators in China being lost. In July 2023, developments in generative AI contributed to the 2023 Hollywood labor disputes. Fran Drescher, president of the Screen Actors Guild, declared that "artificial intelligence poses an existential threat to creative professions".
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Full-featured multi-format Help generator